The article provides broad insights on design for e-commerce websites and mobile applications in business from the perspectives of UX and UI: recommendations and methods to consider.
“Commerce transforms the fate and genius of nations,” well-known British author and scholar Thomas Gray once said.
The business has had hundreds of new avenues to reach customers for the last decade, thanks to technological progress and its expanding significance in everyday life.
As more buyers choose the convenience of online shopping, more merchants open new channels and strategies to capitalize on this trend.
And it is in this domain that the design of a positive user experience directly leads to revenues for stakeholders. In this article:
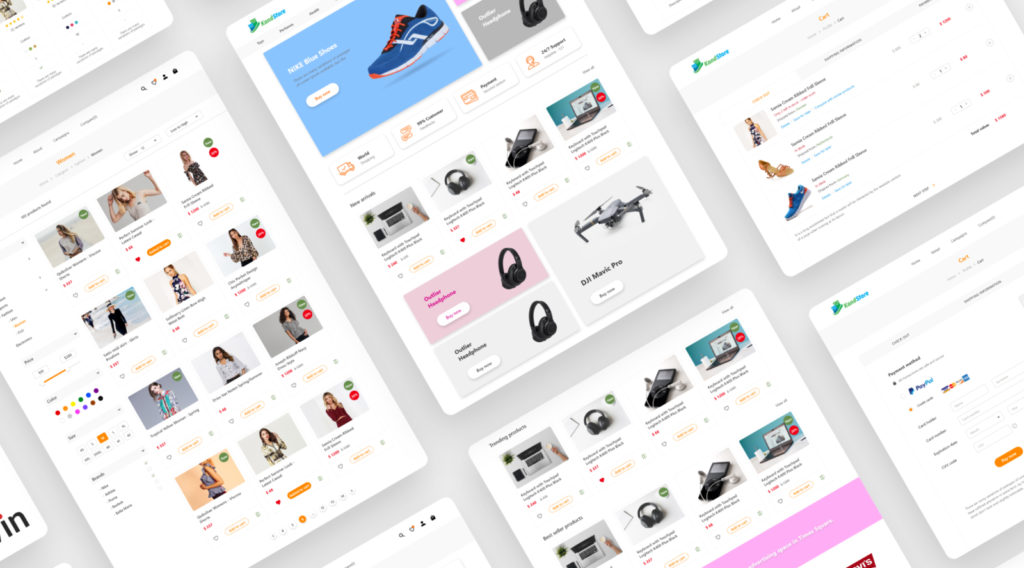
What is eCommerce?
In general, e-commerce (Electronic Commerce) is the direction of company activity when providing clients with goods or services is done through electronic devices and the Internet, as we explained in our free booklet “Design for Business.”
This type of communication and sales closing adds new aspects to data management, sales channels, advertising, and presenting goods and services and enables a complete cycle of commercial operations, such as payments, delivery, and refunds.
The last decade and the recent pandemic saw explosive growth in e-commerce. Today, it facilitates e-commerce from businesses to buyers and online auctions and user-to-user sales platforms.
Today’s e-commerce systems and activities include presenting and booking a wide range of services, e-banking, commercial operations with e-money and e-wallets, many forms of e-marketing, and many other things customers use daily.
The role of design for e-commerce

«If you provide a terrific experience, clients will tell their friends about it. «Word of mouth is mighty,» argues Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos, and disagreeing is difficult. The success of e-commerce activity is dependent on several elements, including:
— the quality of the given product or service
— the quality of the content presenting the offer to customers
— the quality of design for the electronic platform — website and/ mobile application — through which the sales will be delivered
So it’s clear that the UI/UX design aspect is critical. Thoroughly thought-out logic and transitions, simple and clear microinteractions, quick system feedback, pop ups, appealing product presentation, simple payment flow, and a plethora of other details and features can directly impact increasing profits for the business involved in such a popular e-commerce game.
This is where designers and business specialists may collaborate as one team for the benefit of everyone, most notably the target users.
Designers should take the following factors into account while creating an e-commerce site or mobile app:
- strong branding
- security of users’ data
- operational simplicity
- Web design that supports the offer, not overshadowing it.
- effective use of visual headers
- clear data presentation via menus, catalogs, etc.
- user’s capability to leave feedback about goods and services
- readily available general and contact information about the business providing goods or services
How can I implement e-commerce?

You should consider the following factors if you want your online store to be a huge success and not work against you.
Simplicity – Make your website user-friendly and straightforward. This implies that it should just take a few clicks for your clients to buy a product—the fewer clicks, the better. Customers will like your website.
Navigation – Your website should be designed and organized to make it simple for potential customers to locate the products they’re looking for. You will likely lose a consumer who spends a lot of time searching for a product on your website. Make sure the navigation on your e-commerce site is simple so that customers can quickly locate what they’re searching for.
Stability – Your website should load quickly, crash infrequently or never, and be stable. Make sure your website is functionally sound for users. If the transaction procedure is complex, customers won’t buy your stuff.
Security – Assure your consumers that their financial and other sensitive information, such as contact details and physical addresses, are safe when they make online purchases. Websites are vulnerable to hacking and data leaks. Aim to avoid being a victim. You may put a clear privacy statement on your website regarding who has access to your customers’ information to protect it from hackers.
Credibility – Maintaining connections with clients and other business associates is crucial, regardless of the sort of business you are running.
Due to the absence of face-to-face communication, building and maintaining these connections can be challenging for e-commerce.
Let your company strive for professionalism and trustworthiness in your internet marketing and website to overcome this difficulty.
You may get consumer feedback so that prospective buyers can compare their experiences with those of others who have tried the product and make an educated choice.
Mobile optimization – Keep in mind that your clients access and purchase your services and products online. Make sure clients visit your website and purchase using their mobile phones or other mobile devices.
If you are utilizing a custom-built website, make sure to communicate to the web developer your desire for the website to be mobile-friendly. Make that the host of a hosted solution supports mobile sites.
Business Perspective: Branding and Promotion
Websites and mobile device applications for e-commerce are (or should be) always the products of a specific business model. It means they are a part of a precise company plan with specific goals in mind and approaches to attain them.
As a result, the design for this type of product begins long before the first genuine line appears on paper or computer.
Before the actual design begins, numerous critical concerns must be examined and agreed upon. We might list the following as examples:
| The product’s unique selling point. | It is critical to determine which advantage (or group of benefits) will distinguish this website or application from others and make it the primary value expressed through responsive design. |
| Designated target market. | It is critical in e-commerce to identify who your buyers are from the beginning of the project. Designers can be more exact in searching for the shortest path to a successful purchase if they know their age and culture, potential difficulties and wishes, level of computer literacy and faith in the idea of the online store, social circles influencing them, and components defining their habits. |
| Marketing and sales channels. | It is difficult to immediately establish all channels for selling and promoting the future product, but successful company planning requires considering their core from the outset. It will allow the design team to track and support the consistent experience of accessing and interacting with the product. |
| The average usage setting. | Designers must understand when, where, and under what conditions users will typically use the website or app: these factors have a significant impact on decisions about layout, color scheme, typography, transitions, and interactions, all of which must have the overall goal of making the shopping process easy, quick, and enjoyable. A good example is Shopify. |
UX perspective

Regarding e-commerce, it’s critical to recognize that selling the goods once through a website or mobile application is the most basic course of action.
Business stakeholders want this consumer to keep buying from their website or app.
Profit growth is a direct result of user retention. And we must accept that this characteristic makes the e-commerce sector more appealing to designers.
The goal should be obvious and straightforward: customers should visit the e-commerce platform and purchase things from it.
Make no mistake: a great user experience is essential for user retention. In the case of e-commerce, the four most important parts of UX are apparent:
- The product’s utility is inherent in its design: it assists users in selecting and purchasing the goods and services they require.
- Usability must make the consumer journey evident and straightforward, with no extra clicks, time wasted on loading overloaded sites or complicated menus, irritation from not receiving feedback from the system, and so on.
- Accessibility must emphasize design that can be used by many user groups, such as those with disabilities (dyslexic, colorblind, etc.) or with a low degree of tech literacy.
- Desirability indicates that the app will have a look and feel that will make the experience delightful and users want to return.
Intuitive navigation
You can have a great website with a modern and trendy design and gorgeous images, but its success will not be evaluated by the number of “wows” it generates.
The quantity of completed purchases is used to calculate efficiency. If users do not buy, the design is meaningless, and stakeholders lose money.
The premier violin here is transparent, simple navigation. Users must comprehend a variety of elementary concepts at each stage of interaction, such as:
- what firm or brand are they working with
- what page are they on
- where the menu is located, how they may return to the home page or catalog
- where the search engine and filters are located
- how long the page-loading time will take
- how will they be able to read the extensive information about the item
- how will they be able to choose amongst options for the same thing (color, size, etc.)
- how they can pay/ checkout for the item
- how they can save the goods they want to return later
- how they can contact the seller
- how they can examine the ratings and reviews of previous buyers, and so on
Sales funnel
A sales funnel (also known as a purchase funnel) is a technique that guides the consumer through multiple levels of involvement, offering required information about the product and benefits and convincing him/her to make a purchase.
As previously stated in the book, the typical sales funnel consists of the following stages:
- Introduction (Awareness). The user is given basic information on the product, including its brand name and nature. In other words, the user discovers that the product or service is available.
- Education (Interest). The user is given more thorough information on the characteristics and benefits of the product or service that may be of interest to them and may be able to solve their problems.
- Evaluation (Analysis). The user has the opportunity to compare the offer to its competitors and learn more about the product or service’s USPs (Unique Selling Points).
- Decision (Engagement). The user receives final critical arguments to persuade him or her to make a decision; this can include a summary of the offer’s primary benefits, information about further bonuses or special offers, compelling call to actions (CTA), and an explanation of the purchasing process.
- Purchase. The user makes a selection and accepts the ability to purchase something. The transaction has been completed.
- Retaining (Repeating the experience). The user can leave comments, obtain additional contacts supporting the offer, subscribe to updates, and quickly repeat the purchase if desired.
In terms of e-commerce business, the sales funnel is backed up by a wide range of features that digital items can provide.
Customer-centric, informative, and engaging design solutions result from understanding the concepts of sales funnels.
The sales funnel can be fully represented on the website or landing page, as well as in a mobile application, or it can come from an external source, such as social media, which takes over the task of raising awareness and guiding engaged visitors to a platform where people can buy.
Effective presentation of the items
Another important consideration is the arrangement of the product pages or screens.
On the one hand, it’s best not to cram too much information onto the page, as this can overwhelm customers and divert their focus away from the main purpose – making a purchase.
On the other hand, users are unwilling to navigate from one page to the next to obtain additional information on the item.
As a result, the designer must devote time to conducting thorough research on the subject and determining the appropriate balance of material presented on a single screen.
User testing and target audience analysis can provide insight into what information the target audience requires for various commodities or services.
UI perspective
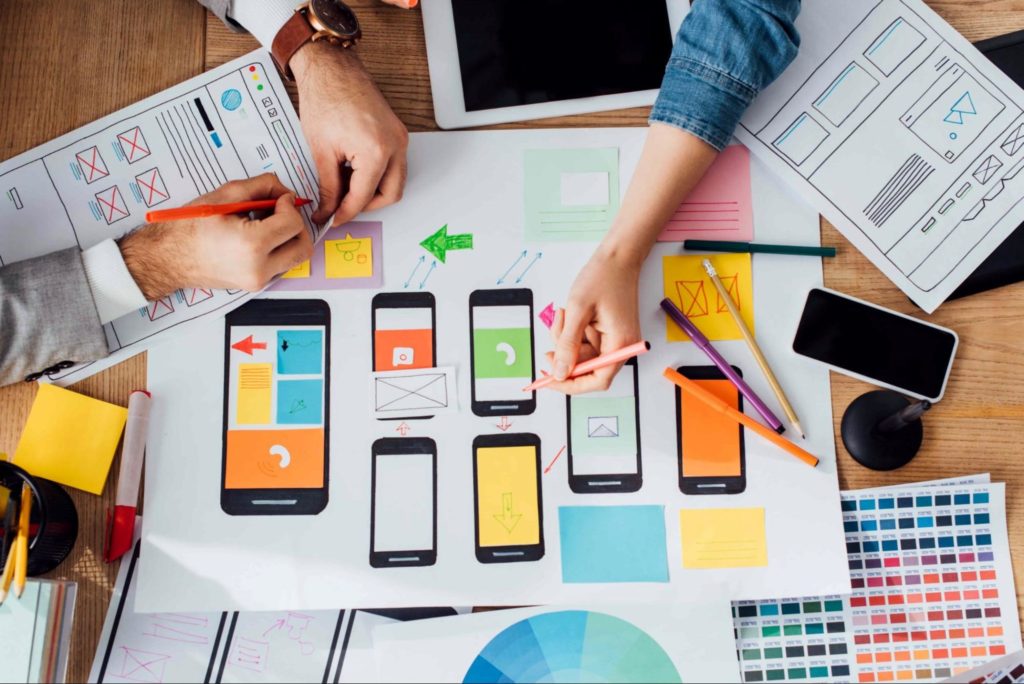

The UI design stage, which focuses on logic, transitions, looks, and style, is critical to the e-commerce project’s success.
It is the aspect that provides visual performance and lays the foundation for the interface’s appeal and good buyer emotional input.
Designers must find a basic stylistic approach that will support the UX criteria described above and offer the online point-of-sale a pleasing appearance during the UI design stage for e-commerce.
The following are some considerations that designers must make in this regard:
- Bright Colors that are in line with the brand’s image and that amplify emotional feedback
- Determining a style that is appropriate for the nature of the business offer: People should be able to tell right away if the website sells domestic goods, fresh veggies, stylish clothes, rare technology, or anything else.
- The primary zones of engagement are immediately visible thanks to a visual hierarchy.
- The general harmony of perception sets the feeling of aesthetic satisfaction that supports a positive customer experience.
Points to consider
Finally, here’s a quick checklist for some key factors that designers should consider when working on e-commerce projects:
- User research will assist in determining the wants and desires of the target audience.
- Make sure users are well-informed: load the screens or pages with the information and functionality they require to make a purchase.
- Keep the design consistent: not only does the website design or app need to be consistent in terms of basic branding across all devices, but so do social media, print materials, and any physical point-of-sale appearances if they exist.
- Refresh the experience: tiny adjustments or beautiful touches added to the interface from time to time without disrupting the overall aesthetic consistency can provide a sense of renewal, similar to how new looks of mannequins in shop window displays can.
- Examine your options: user testing can help you better understand the aspects influencing conversions. It should ideally be used not only during the design phase but also after the introduction of the e-commerce platform, based on real-world user interactions, what-are-e-commerce-advantages-and-disadvantages,/and potential problems.
- Be wary of revolutions and the “wow” effect: the force of habit plays a massive part in this type of product. Choosing a layout, menu, or icon that is too different from what users are used to can cause confusion and frustration.
- Respect the buyers: remember that these aren’t abstract numbers – each figure on a conversion report represents a real person. Look for an interface that will respect their time, effort, and needs, resulting in a great buying experience for all parties.
What is a marketplace for online loans?
A relatively recent kind of internet lending is marketplace lending, sometimes referred to as peer-to-peer or platform lending.
It makes use of internet platforms to link lenders and borrowers, whether they be companies or individuals.
The platform typically collects principal and interest payments from borrowers once a loan is completed and transfers the funds to investors, less any fees the platform retains.
Platforms for marketplace lending typically promote new loans and loans that may be used to pay off previous debt.
Top 10 UI Trends

1. Branding with unique illustrations
You name it: digital or hand-drawn, 2D or 3D, custom illustrations. Free shapes, components, unaligned pieces, and enormous asymmetry help platforms stand out from the crowd and set up a welcoming and friendly environment that improves user experience.
These graphics are typically brought to life with elaborate motion design to make these pages stand out. This vitality makes it easier to grab the user’s attention and quickly explain what the company or brand offers. A fun graphic may give a website or mobile app a personality and make it more memorable.
Nonetheless, we must watch these daring solutions and consider the web’s business.
Whenever a modification is done, it should be tested to see how efficient it is in conversion rates.
A service website can still appear modern and professional if used correctly, minimalistic with a touch of elegant 3D artwork.
2. Custom cursor interactions
Micro animations and flamboyant, over-the-top interactions are frequently used on websites to make them stand out.
We’ve all seen intriguing gimmicks and oddities that entice us to explore every last element of a website.
One of the most suitable interactions is when my cursor movement is used as an input, resulting in vibrant and entertaining consequences.
3. Delve into the Metaverse
Since Facebook rebranded as Meta, there has been much speculation about what the future holds for how we connect and settle in the Metaverse.
Metaverse, for those unfamiliar, is a mix of technologies such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and video in which users “live” in a digital domain.
Its supporters call it the “new internet” and believe it has immense promise. The AR/VR market will explode if Meta’s strategy is successful.
Meta plans to lower the price of their Oculus headsets, such as the Quest. A larger market size necessitates a greater emphasis on developing new experiences for those platforms, which might lead to new chances for UX/UI design.
It represents a new horizon for technological advancements and innovation. These User Interface trends will push users to look beyond the box rather than stick to the grid.
Forget about user interfaces that are displayed on a screen. Instead, prioritize encounters that feel like they’re taking place in real life.
4. Utilizing 3D in e-commerce
3D has been around for some time and is gaining popularity steadily. Thankfully, we live in a period where tremendous breakthroughs in semiconductor manufacture and software optimization over the past decade have enabled even low-end devices to process complex images in real-time.
Consequently, utilizing dynamic 3D UI is no longer laborious. On web pages, animated elements such as logos, graphics, and text will increase, allowing users to differentiate between interactive and non-interactive features.
E-commerce is one of the most efficient means of incorporating 3D into a digital product. As the market switches to the online arena, marketers create inventive methods to lure consumers into purchasing their products.
5. Bolder and more characteristic fonts
Because most styles are adapted to specific businesses, font trends aren’t particularly fascinating to discuss. Serif fonts are popular in fashion and note-taking apps, whereas sans serif fonts are popular in computers and other products.
The two trends are brands beginning to embrace and adopt the aesthetic of significantly bolder fonts and ink trap typefaces in their UI.
6. Low code & no-code platforms
In recent years, low-code and no-code software have grown in popularity. These systems require a basic understanding of programming (Low code) or none (No Code).
They allow you to construct your own website even though they require industry experience. There are several online visual editors available that allow users to create and publish their websites.
Webflow was also used by one of our talented designers to create our newest product, Archifolio. Archifolio is a personal website builder for architects that makes it simple to develop their unique brands and advance their professions.
Rather than seeing the same template on multiple websites, users may create even more original and creative pages with it.
7. Dynamic color palettes
Android 12 was unveiled alongside Material You, a new user interface from Google. Apart from a significant overhaul, our most notable feature was dynamic color palettes. This means you’ll be able to modify the look of your smartphone further.
It’s easy to use: it generates a palette based on your wallpaper that matches it in terms of color, hue, and tone, resulting in an attractive and harmonious result.
8. System-like UI
Please bear with us if this appears to be a long shot. One of Google’s engineering leads, Jeff Verkoeyen, disclosed that the company’s iOS apps would no longer use Material Design user interface components, instead opting for Apple’s own UIKit.
UIKit now provides most of the components required for Google apps, according to him. Rather than specialized coding, investing in the long tail of UX elements helps apps to feel even better on Apple platforms.
The technological decisions made by Google and Apple have an evident impact on other firms.
9. Storytelling with scroll-triggered animation
Among the best, the capacity to tell fantastic stories based on a digital experience will remain popular. By itself, typography can generate a strong visual hierarchy. It’s a crucial part of the user interface and contributes significantly to a positive user experience.
Since copywriting has emerged as one of the essential parts of a positive user experience and will continue to do so in the coming year, text layout alone will not be sufficient.
The narrative engages customers with a brand by making them feel like they’re a part of the story, while the style draws them in.
As a result, users using mobile devices are less inclined to skim the text. Don’t underestimate the value of UX authoring.
10. Designing for foldable
Samsung had a terrific year in terms of folding devices. The Z Fold and Z Flip 3 sold more than their predecessors.
As technology improves and becomes more accessible, other manufacturers will want to thrive in this market. Therefore software will need to change quickly.
With the release of Android 12, Google built a Material.io subpage that outlines all of the criteria and constraints that must be considered while creating apps for foldable screens.
FAQs
What is SEO (Search Engine Optimization)?
Search engine optimization is the process of improving your website to increase its visibility when people search for things or services related to your business on Google, Bing, and other search engines.
The higher your pages appear in search results, the more probable you will draw attention and new and existing customers to your business.
What is Bounce Rate?
The percentage of guests that leave a webpage without acting, such as filling out a form, clicking on a link, or making a purchase, is called the bounce rate.
What is an algorithm?
A process for solving a problem or completing a computation is referred to as an algorithm. Algorithms are precise sets of instructions that perform specified operations in either hardware or software-based processes.
What is an Application Programming Interface (API)?
Application programming interface (API) is a term that refers to a set of tools that A software intermediate, or go-between, is a program that allows two programs to connect. APIs are used every time you engage on Facebook, buy anything on Amazon, or read the news on your phone, for example.
Author Bio:

Jonathan Aisiki is a Senior Writer at MarketingForCustomers.com. He writes B2B articles and creates SaaS marketing content that delivers visible results. He aims to educate and offer readers as much unique value as possible.




